Birds

Endangered
facts

They also eat small mammals like mice, some reptiles, and amphibians.

description
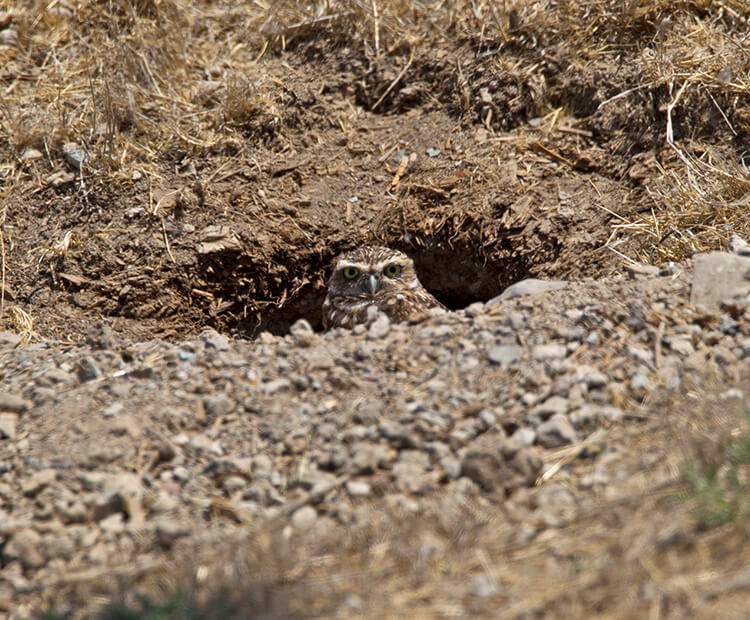

Whoooo's special?
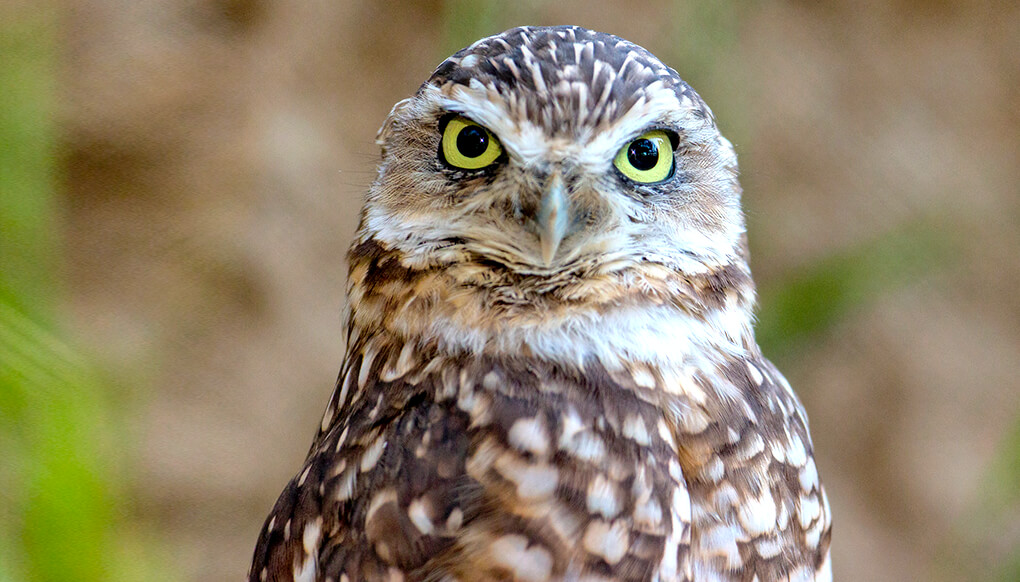
This small bird, found in North and South America, is different from most other owls. While other owls are active only at night, a burrowing owl hunts during the day as well as at night. Instead of nesting in a hollow high up in a tree, it nests in an underground burrow. But it doesn't dig the hole itself! Burrowing owls take over holes and tunnels dug by ground squirrels, prairie dogs, armadillos, tortoises, and skunks.
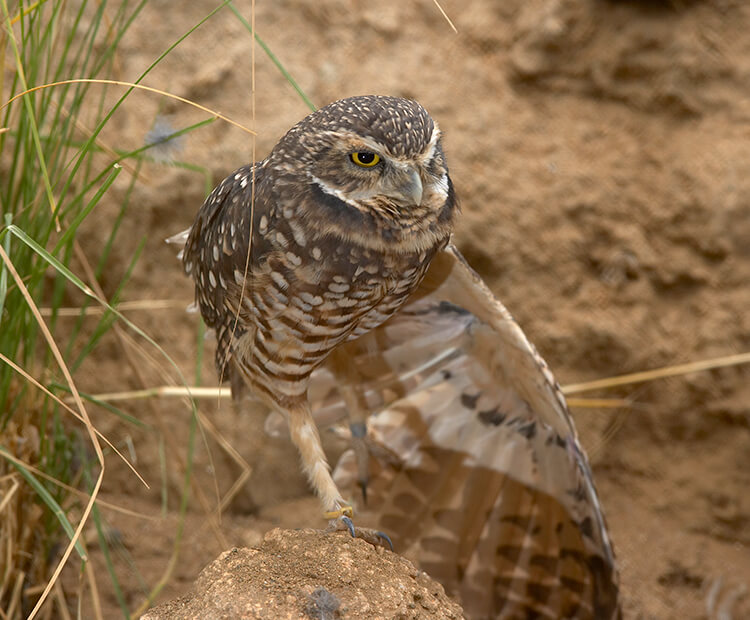

The best nest
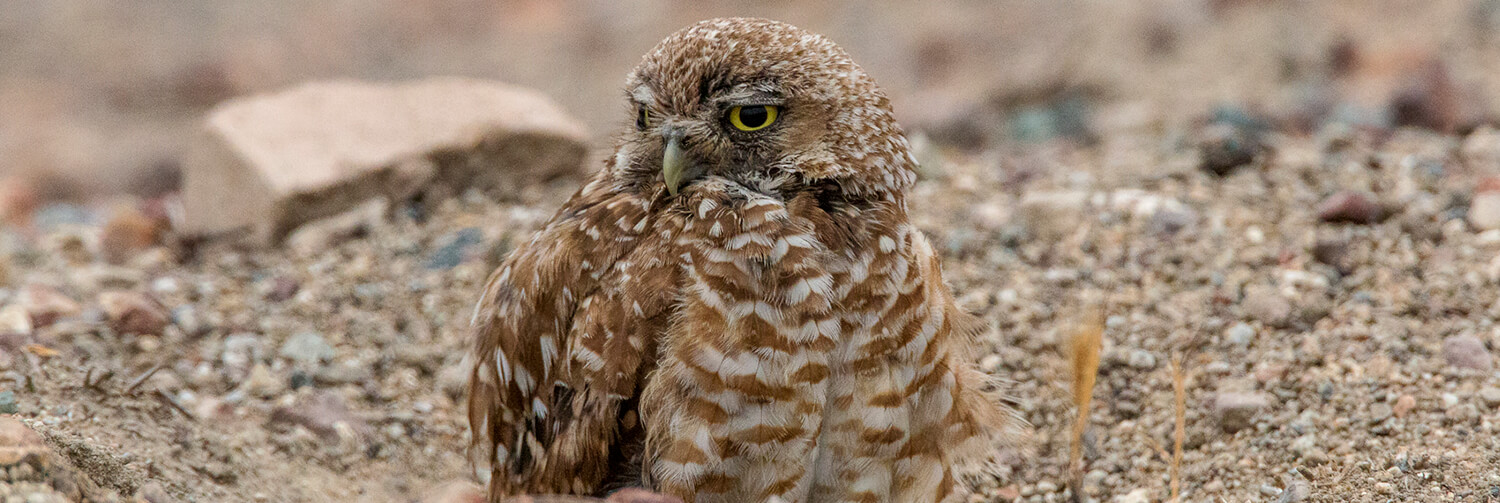
When they move into an abandoned burrow, these little owls do some "decorating." They gather grass, feathers, and even chunks of animal dung and line their underground home with it. They also leave some just outside the entrance. Biologists think the items might help keep the inside of the tunnel at just the right temperature. The dung outside would attract insects that the owls can eat.
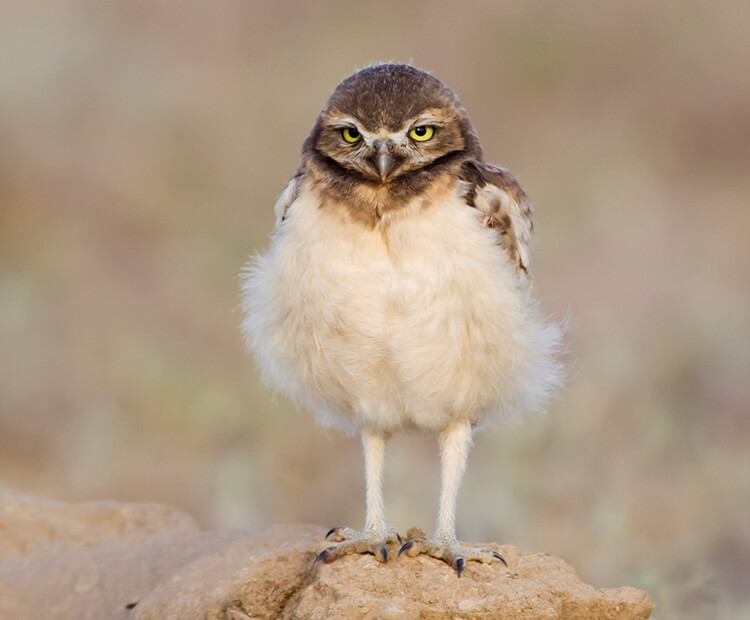

Growing up owl
A female burrowing owl lays about 3 to 12 eggs in her burrow. She sits on the eggs for about 1 month until they hatch. Her mate stands guard outside the burrow and brings her food. The young chicks stay in the burrow for about 2 weeks before they start stepping outside. Their parents bring them insects to eat and practice pouncing on. When they are about 6 weeks old, the little owlets begin to fly and hunt their own meals.
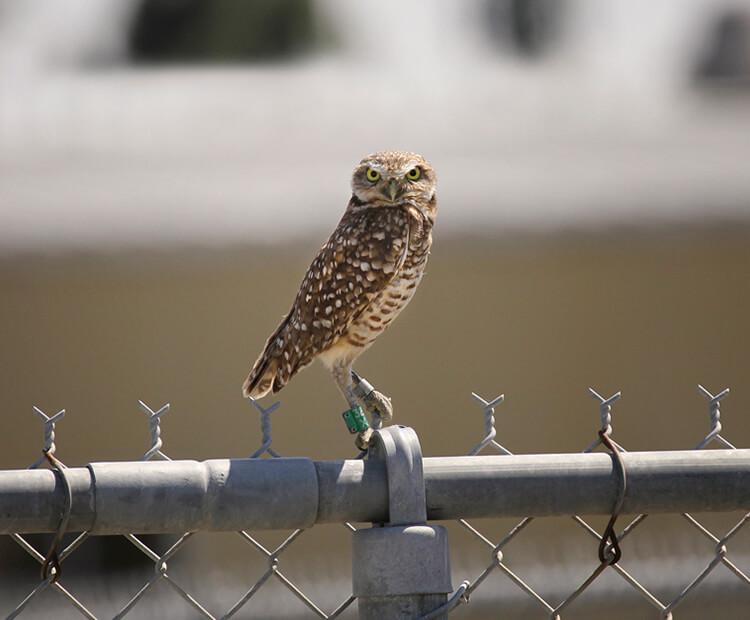

Hold that habitat!
Burrowing owls live in wide, flat habitat like grasslands and even fields near cities. When parking lots, shopping centers, and big blocks of houses are built, they may lose their homes and hunting grounds. Pesticides hurt these birds, too, because they eat insects.
San Diego Zoo Global gives a hoot about these birds. We have a group of scientists working on understanding what burrowing owls need in their habitat. We will be able to use this information to help protect habitat for these tiny predators.















